الصورة العامة - y' = F(x,y)
or
M(x,y)dx + N(x,y)dy = 0
1- Separable equations :
ويتم فيها فصل x عن y (فصل المتغيرات)
to solve the separable equation :
1. set y' = dy/dx
dy/dx = f(x)g(y)
2. dy/g(y) = f(x)dx
3. by integration we obtain the solution .
:: Special case ::
- If the DE in the form y' = F ( ax + by + c )
to solve this equation we set [ ax + by + c = z ]
2- Homogeneous equations :
F(x,y) is called homogeneous of degree if F( tx, ty ) = tn F(x,y)
إذا كان كل حد من حدود المعادلة من نفس الدرجة تبقى homogeneous
or x/y or y/x
a DE M(x,y)dx + N(x,y)dy = 0
is called homogeneous if M(x,y) & N(x,y) are homogeneous of the same degree
To solve the homogeneous DE :-
1. set y = vx
2. y' = v + xv'
3. بالتعويض هاتتحول المعادلة الى separable
:: Differential Equations reducible either separable or homogeneous ::
if the differential equations in the form
a1x + b1y + c1
y' = ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
a2x + b2y + c2
1- parallel :
if a1/b1 = a2/b2
we set
a1x + b1y = z
or
a2x + b2y = z
then the equation is reduced to separable .
2- intersection :
if a1/b1 != a2/b2
we solve the two equation to find the point of intersection (h,k)
then
we set x = t + h , y = s + k
and dy/dx = ds/dt
by substitution , the equation is reduced to homogeneous .
:: Exact differential equation ::
A DE M(x,y)dx + N(x,y)dy = 0 لازم موجب
if dM/dy = dN/dx the equation is called exact .
the solution of the exact DE is in the form

حيث xo , yo قيم ابتدائية اختيارية يتم اختيارها على اساس جعل المعادلة أسهل ما يمكن ولا تعتمد على بعضها وعادة ما نختارها بـ 0 أو 1 في حالة ln
:: Integrating Factor عامل المكاملة ::
if dM/dy != dN/dx the DE is not exact .
- we can transform this equation to exact by multiplying it by integrating factor M ميو
- to find the integrating factor - two cases :-
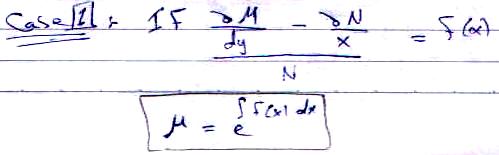
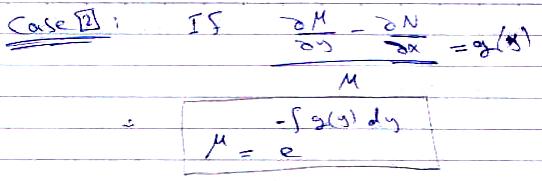
:: Linear differential equations ::

:: Bernoulli 's equation ::

___ , ___ , ___ , ___
___ , ___ , ___
___ , ___
___
,